Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications often require significant computing resources and produce substantial data. However, transferring and processing this data in a traditional, centralised data centre can be slow and expensive due to network latency and bandwidth costs. This is where edge data centres come into play. AI is a foundational computer technology which promises to bring enormous benefits to society. Some applications using AI need to be placed near the users – these are called Edge AI.
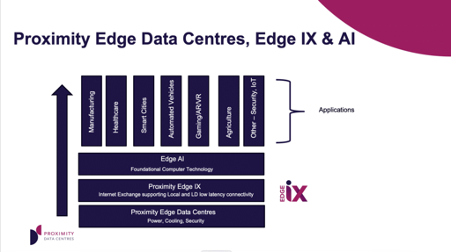
Here’s why Edge AI requires Edge Data Centres:
In summary, AI can greatly benefit from edge computing and edge data centres because of lower latency, improved bandwidth use, enhanced security, increased reliability, and scalability. This is why many companies are investing in edge computing infrastructure to support their AI applications.
1. Latency Reduction: Edge data centres are designed to be located closer to the users & devices that generate and consume data. This proximity significantly reduces the distance data must travel, which significantly lowers latency and provides faster, real-time responses. This is crucial for AI applications that need to process data and make decisions in real-time, like autonomous vehicles or IoT devices. These work best in junction with regional internet exchanges which avoid the ‘tromboning’ of data over hundreds of miles.
2. Bandwidth Efficiency: Transferring data between devices and a centralised data centre can consume substantial network bandwidth, potentially leading to network congestion and increased costs. By processing data locally in an edge data centre, AI applications can use bandwidth more efficiently and reduce the volume of data that must be sent over the network.
3. Power and Cooling Requirements: AI infrastructures are very powerful and consume enormous amounts of power and need high levels of cooling. The power consumed in a single rack can be staggering and in some cases exceed 50 kWs. Only purpose built & designed data centres can provide the right level of secure power and cooling required.
4. Security and Privacy: Some AI applications handle sensitive or private data that must be protected. Processing this data locally in an edge data centre can reduce the risk of data breaches by minimising the amount of data sent over the long distance network. It also allows for better compliance with data sovereignty laws which mandate certain types of data to be stored and processed within specific geographical locations.
5. Reliability and Redundancy: Edge data centres can continue to operate even if the network connection to the centralised data centre is lost. This can be vital for AI applications where constant uptime is necessary, such as healthcare or industrial automation.
6. Scalability: Edge data centres provide a way to increase capacity as needed without significantly impacting the centralised infrastructure. This is useful in scenarios where the amount of data being generated is growing, as is often the case with AI applications.
7. Internet Exchanges: Edge data centres designed to be connectivity hubs and support local internet exchanges help avoid network latency and optimise networks to deliver the best user experience for the AI application.
Read our part 2 edition to this series about Edge Data Centres and AI:
– Guest Blog authored by John Hall – Managing Director, at Proximity Data Centres

